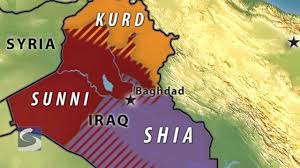
(AhlulBayt News Agency) - Since the Ottoman Empire’s governance over Iraq in the midst of the fifteenth century, until the collapse of the authoritarian regime of Saddam Hussein in 2003, the power has been in the hands of Sunnis. With the collapse of the Ottoman Empire and the formation of the government and people of Iraq after World War 1, the governance of Sunnis over Shiites was institutionalized, under the shadow of the British colonialism.
Although the Shiites and Sunnis have peacefully coexisted in Iraq through the centuries, but the government has always had a religious and tribal approach, and has tried to keep power in the hand of the Iraqi Sunnis. Even though during the monarchy (1922-1958) and the republic (1958-2003) a secular system has been ruling over Iraq, but sectarianism and religious discrimination has been woven into the fabric of Iraq’s political system. Due to this situation, majority of the Sunnis do not have a prosperous and privileged position, because for the past eight decades, economic and political power of the country has been exclusively limited to the triangle of Mosul, Anbar, and Samarra. The elites of the Anbar province have had a larger share of the power, especially in the era of Saddam Hussein (1979-2003).
But with the fall of Baghdad, the collapse of Saddam Hussein's regime in April 2003, and 10 years of US occupation, opportunity arose to improve the Shiite majority’s position.
During the years that Shiites started getting power, despite the propaganda and media coverage, Shiite political elites and movements never had a sectarianism approach, in fact, no efforts or policies were made by Shiites, to isolate the Sunni minority in Iraq.
Sunnis and Political Participation
The Sunni political elites have played an important role in the formation of political parties, organizations, and civil society. Sunnis have also had an active presence in various political ideologies; everything from international communism to the Muslim Brotherhood and Salafi-Jihadi mindsets. The presence of these elites in the circles of power and decision making, has significantly helped strengthen the position of Sunnis in Iraq’s politics and parties.
Most of the nationalist and secularist parties were formed by Sunni elites during the monarchy era. These elites also played a big role in the formation of socialist and communist parties, and the Muslim Brotherhood. Sunni elites are currently present in the following parties:
1. The Islamic and Religious Movement
-The oldest religious organization of Sunnis in Iraq is the Muslim Brotherhood. This organization was founded by Muhammad Mahmud al-Sawwaf and Amjad al-Zahawi in 1944. The Iraqi Islamic Party was formed in 1960 as the Iraqi branch of the Brotherhood. After the fall of the Saddam Hussein government, Islamic Party became active and its leader, Tariq al-Hashimi became the Iraqi Vice-President. Al-Hashimi was actively involved in a conspiracy against the Iraqi political system, so he was fired and is now serving the anti-Iraq policies in Ankara and Doha. In the parliamentary elections of 2006, Iraqi Accord Front was formed by the Islamic Party. The Iraqi Accord Front recieved 45 seats in in that parliamentary election. The Islamic Party started to break up over the past decade.
-Association of Muslim Scholars is a scholar organization that was formed after the Saddam Hussein regime was demolished. Harith Sulayman al-Dhari, a cleric at Saddam Hussein’s government, was the chairman of this association. This group has always been opposing the governance of Shiites in Iraq.
-Sunni religious elites and clerics established al-Majma al-Fiqhi al-Iraqi, in order to form a united Sunni authority. If this institution had worked and cooperated with Shiite religious organizations and institutions, it could have achieved national unity for Iraq and the Sunni minority of the country. However, some of the leaders and members of this institution were acting against the interests of Iraqi Sunnis and the general population, which worsened the situation of social gaps in Iraq.
-Sunni Endowment Diwan was formed after the closure of the Ministry of Endowments and Religious Affairs in October 22, 2003. This religious institution handles the endowment affairs of Sunnis.
2. Political and Secular Movement
-Uniters for Reform Coalition (Muttahidoon) is one of the most powerful Sunni political organization. This political coalition was formed in January 2012 by former parliament speaker, Osama al-Nujaifi. This coalition consists of religious/political movements such as the Islamic Party, the Iraqi Nationalist Party, and the Iraqi Turkmen Front. The coalition had a considerable victory in the provincial council elections of 2013.
-Sunni elites have had an active presence in the secular coalition of Iraqi National Movement. This movement is led by Iyad Allawi, and is considered to be a strong rival for the State of Law Coalition which is led by Nouri al-Maliki.
-The Iraqi Front for National Dialogue is one of Iraq’s Sunni political parties and is led by Saleh al-Mutlaq (Born in Fallujah in 1947). This group has influence in the Iraqi government and parliament. Al-Mutlaq disagrees with other Sunni political leaders, Osama al-Nujaifi and Tariq al-Hashimi, on various topics. Misha’an al-Jaburi is a Sunni resident of the Nineveh province. He had been opposing Sadda Hussein and with the change of the political system in Iraq, returned to the country. He leads a Sunni political movement that has influence in the Iraqi parliament and government.
It should be noted that after the fall of Saddam Hussein, the Sunni political community of Iraq has been breaking up. For example, in the parliamentary elections of 2014, 25 parties and coalitions competed against each other in the Anbar province, in order to obtain 15 seats in the Iraqi parliament. With the occupation of Sunni provinces of Anbar, Saladin, Nineveh and Diyala, by ISIS on June 10, 2014, the conflict and gap among the Sunni political community got even worse. On this basis it is clear that creating unity and harmony among the Sunni community of Iraq, is a difficult task.
In the Cabinet of Dr. Haider al-Abadi, Sunnis hold key posts such as the Ministry of Defence. Also, in the Iraqi parliament, led by Dr. Salim al-Jabouri (deputy general secretary of the Iraqi Islamic Party), the Sunnis have several fractions, including:
1. Tahalof al-Qawi led by Salim al-Jabouri and Zafir al-Ani (born in al-Anah city of the Anbar province in 1958)
2. National Movement for Development and Reform led by Jamal al-Karboli
3. Osama al-Nujaifi Supporters affiliated with the Uniters for Reform Coalition (Muttahidoon) which are Sunni Arab tribes such as Shammar, Jubur, Dulaim. These tribes are considered to be the most powerful Arab tribes in the Northern and Western regions of Iraq. They also play an important role in the social components of Iraq.
Iraqi Sunni regimes, over eight decades, have had a key role in the partition of Sunni community and Sunni Arab tribal conflicts. In order to strengthen its power in Baghdad, the Saddam Hussein regime equipped and armed some Sunni Arab tribes such as Tikrit, against the Dulaim tribe.
The fragmentation and splitting of the Sunni political community in Iraq is due to the divisive politics of the West and seditious plans of the Saudis. Sunni community’s cooperation with the modern Iraqi political system, will led to unity and development of the Iraqi government and people. Also, this country will not achieve peace and stability unless Shiites, Sunnis, and other social components in Iraq unify.
/298